Inside Raccoon Stealer V2
Raccoon Stealer is back on the news again. US officials arrested Mark Sokolovsky, one of the malware actors behind this program. In July 2022, after several months of the shutdown, a Raccoon Stealer V2 went viral. Last week, the Department of Justice’s press release stated that the malware collected 50 million credentials.
This article will give a quick guide to the latest info stealer’s version.
What is Raccoon infostealer V2?
Raccoon Stealer is a kind of malware that steals various data from an infected computer. It’s quite a basic malware, but hackers have made Raccoon popular with excellent service and simple navigation.
In 2019, Raccoon infostealer was one of the most discussed malware. In exchange for $75 per week and $200 per month, cybercriminals sold this simple but versatile info stealer as a MaaS. The malware was successful in attacking a number of systems. In March 2022, however, threat authors ceased to operate.
An updated version of this malware was released in July 2022. As a result, Raccoon Stealer V2 has gone viral and gained a new name – RecordBreaker.
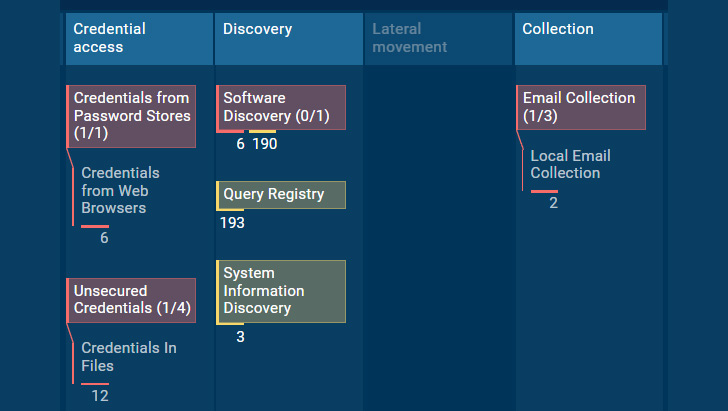 |
| Raccoon v2’s tactics & techniques in ANY.RUN Sandbox |
How to analyze Raccoon stealer V2
|
Execution process |
What Raccoon malware does |
|
Downloads WinAPI libraries |
Uses kernel32.dll!LoadLibraryW |
|
Gets WinAPI functions’ addresses |
Uses kernel32.dll!GetProcAddress |
|
Strings and C2 servers encryption |
Encrypts with RC4 or XOR algorithm, can be no encryption at all, or combination of different option |
|
Crash triggers |
CIS countries locale, mutex |
|
System/LocalSystem level privilege check |
Uses Advapi32.dll!GetTokenInformation and Advapi32.dll!ConvertSidToStringSidW comparing StringSid with L “S-1-5-18” |
|
Process enumeration |
Uses the TlHelp32 API (kernel32.dll!CreateToolhelp32Snapshot to capture processes and kernel32.dll!Process32First / kernel32.dll!Process32Next). |
|
Connecting to C2 servers |
Creates a string: Then sends a POST request |
|
User and system data collection |
|
|
Sending of collected data |
POST requests to C2. |
|
Getting an answer from the C2 |
C2 sends “received” |
|
Finishing operations |
Takes a screenshot(s), releases the remaining allocated resources, unloads the libraries, and finishes its work |
We have triaged multiple Raccoon stealer V2 samples, collected typical behavior activities, and briefly described its execution process.
Read deeper and more detailed Raccoon stealer 2.0 malware analysis. In the article, you can follow all steps and get a complete picture of the info stealer’s behavior. Besides this profound research, you get a chance to extract malware configuration by yourselves – copy the Python script of Raccoon stealer and unpack memory dumps to extract C&C servers and keys.
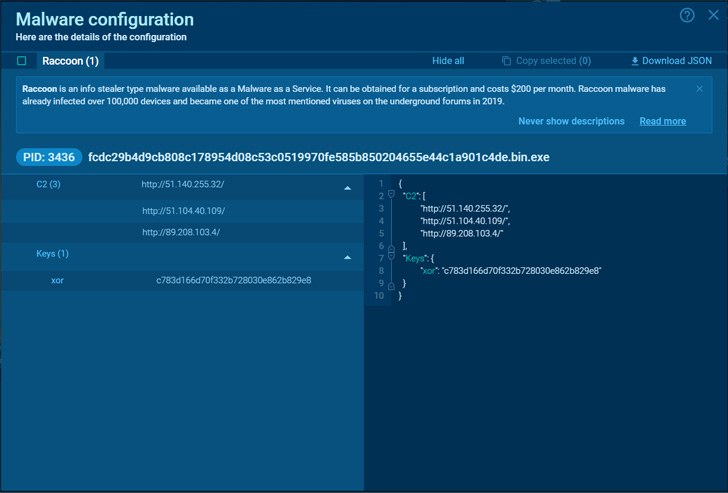 |
| Raccoon v2 malware configuration |
Where to analyze malware
Do you want to analyze malicious files and links? There is a fast and easy solution: get ready-made configurations in ANY.RUN online malware sandbox and investigate suspicious files inside and out. Try to crack any malware using an interactive approach:
Write the “HACKERNEWS” promo code at [email protected] using your business email address and get 14 days of ANY.RUN premium subscription for free!
The ANY.RUN sandbox lets you analyze malware quickly, navigate through the research process easily, detect even sophisticated malware, and get detailed reports. Use smart tools and hunt malware successfully.